Minikube Deployment
Run TrustGraph in a local Kubernetes cluster for production-like development and testing
Intermediate
30 - 60 min
- Machine with 14.5GB RAM and 9 virtual CPUs / threads available for TrustGraph to use - a 16GB laptop is going to be too limited
- Minikube installed and configured
- kubectl command-line tool
- Python 3.11+ for CLI tools
- Access to an LLM (cloud service like VertexAI, AWS Bedrock, or local with Ollama)
- Basic command-line and basic Minikube familiarity
Launch a complete TrustGraph environment in a local Kubernetes cluster using Minikube for production-like development, testing, and learning.
Overview
Minikube is a tool that runs a single-node Kubernetes cluster on your local machine. It’s designed for developers who want to learn Kubernetes or test applications in a Kubernetes environment without needing access to a full cloud-based cluster.
Running TrustGraph on Minikube provides a production-like environment for development and testing. This deployment method offers:
- Kubernetes-native deployment with local development capabilities
- Production-like environment for testing in a more realistic environment than Docker Compose.
- Resource isolation and management
- LoadBalancer and service discovery testing
This is a good way to learn TrustGraph in a Kubernetes environment before deploying to production clusters, or to test Kubernetes-specific features locally.
We also describe a Docker Compose/Podman Compose deployment. The Minikube deployment requires more resources for the cluster.
Getting ready
System resources
As mentioned above, you need a machine with at least 14.5GB of RAM and 9 CPUs available for TrustGraph. That means if you’re running other significant workloads on it, it will probably fail. A 16GB device is too limited.
A Kubernetes deployment is a little more demanding than a Docker Compose deployment, because:
- With a Kubernetes deployment, there are Kubernetes system services which are deployed alongside your application, and count as part of the resource requirement.
- Kubernetes has a stricter resource allocation mechanism when resource constraints are defined. The Kubernetes resource allocation approach has a major advantage for production / persistent deployments because there are guarantees that the resources are available as the system gets loaded.
You can also deploy an instance to your favourite cloud provider, and run Minikube on that if you don’t have a device with enough resources.
This has been tested with Linux. Minikube will run on MacOS and Windows, but it has not been tested.
Python
You need Python 3.11 or later installed for the TrustGraph CLI tools.
Check your Python version
python3 --version
If you need to install or upgrade Python, visit python.org.
Minikube and kubectl
You need to have Minikube and kubectl installed:
Minikube requires a driver for virtualization. Minikube supports many driver types - the level of support and maturity differs between them. Docker is commonly used. We’ve had most success with the kvm2 driver. This has been supported by Minikube for a long period. The podman driver has been well supported for a while.
Large Language Model
You need to have access to an LLM. TrustGraph can work with many different kinds of LLM. You can use a cloud-hosted service, or have an LLM hosted locally on your device or network. TrustGraph can work with small models which you can run on standard home/office equipment, but small models are still demanding on resources. A 16GB laptop is able to run an LLM but likely not at the same time as running all the containers which make up a TrustGraph deployment.
Here are some example ways to get an LLM to run:
| Provider | Description | Access type |
|---|---|---|
| Google Cloud VertexAI | This is a subscription-based service which is part of Google Cloud. The Gemini models are good and cost-effective. There are free credits for new users. | Cloud subscription |
| AWS Bedrock | Amazon’s managed LLM service with Claude, Mistral, and other models available. Running Claude on Bedrock is a good option. | Cloud subscription |
| Azure | Microsoft’s cloud subscription services include Machine Learning Services (MLS) and Cognitive Services (CS). The TrustGraph Azure integration can use the MLS service, while Azure OpenAI can use CS models. | Cloud subscription |
| Anthropic Claude | Integrates with Anthropic’s APIs directly for access to the Claude models. Claude models are very capable. | API subscription |
| Mistral AI | Integrates with Mistral’s APIs directly for access to the Mistral models. | API subscription |
| OpenAI | Integrates with OpenAI’s API for GPT models | API subscription |
| Ollama | Run models locally on your machine. Supports Llama, Mistral, and many others. | Self-hosted |
| vLLM | The most comprehensive self-hosted model engine | Self-hosted |
| LMStudio | Desktop application for running local LLMs with an OpenAI-compatible API. LMStudio is a very user-friendly experience, which makes it easier to diagnose and solve hosting problems. Note: LMStudio is free, but only for non-work-related use. | Self-hosted |
Using a cloud-hosted service is a good starting point - you will need a subscription, but no extra hardware. If you do want to run an LLM locally, you will need a device with a good GPU, and likely some experience of running this yourself as you may need to debug model / hosting issues.
A word on networking and self-hosting
If you are self-hosting a model on the same device you are intending to run Minikube, you will need to understand how to get TrustGraph to talk to your model service.
Minikube has many options for how things are deployed, so it is beyond the scope of this guide to cover all of them. Minikube works by using a virtualisation system to run the container engine, but there are several layers:
- The host device, that runs everything, including desktop apps if you are on a desktop device.
- Minikube runs a virtualisation layer on the host, there are many options for the virtualisation layer, including Docker.
- The virtualisation layer is used to run a container runtime, and there are several options for that as well, including a Docker runtime.
- The Kubernetes control play and various Containers run inside this container runtime.
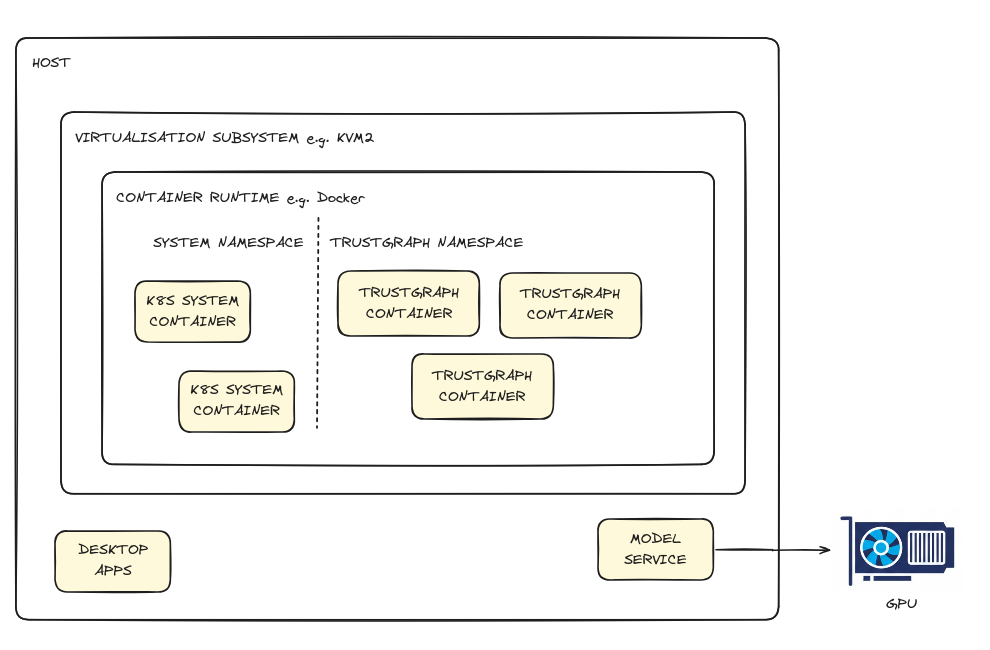
It’s too complicated to explain all of the intricacies that emerge from this arrangement. Minikube simplifies host access by making the hostname host.minikube.internal map to the host from within containers. So, to access ollama on your host machine on port 11434, you would configure access to the address
http://host.minikube.internal:11434
Prepare the deployment
Start Minikube
Minikube needs to be started with enough resources. As mentioned earlier, this is roughly 9 CPUs and 14.5GB of memory. You can specify the virtualisation driver here. Minikube supports many virtualisation mechanisms, KVM2 is the driver we have used with most consistent results.
minikube start --cpus=9 --memory=14848 --driver=kvm2
Startup looks something liek this:
😄 minikube v1.37.0 on Ubuntu 25.10
✨ Using the kvm2 driver based on user configuration
👍 Starting "minikube" primary control-plane node in "minikube" cluster
🔥 Creating kvm2 VM (CPUs=9, Memory=14848MB, Disk=20000MB) ...
🐳 Preparing Kubernetes v1.34.0 on Docker 28.4.0 ...
🔗 Configuring bridge CNI (Container Networking Interface) ...
🔎 Verifying Kubernetes components...
▪ Using image gcr.io/k8s-minikube/storage-provisioner:v5
🌟 Enabled addons: storage-provisioner, default-storageclass
🏄 Done! kubectl is now configured to use "minikube" cluster and "default" namespace by default
By default, Minikube deploys 20GB of storage for the Kubernetes deployment. You can change this with the --disk-size option.
When Minikube starts, it configures access to the Kubernetes cluster in your default ~/.kube/config so that you can use kubectl to access the cluster.
Verify Minikube
You can check the status of the Minikube cluster:
minikube status
You can check the status of the Kubernetes cluster:
kubectl cluster-info
And see the nodes. Minikube only supports a single node:
kubectl get nodes
Create configuration
Use the TrustGraph Configuration Builder to generate your deployment configuration. By default, the configurator selects the newest stable deployment. To be compatible with this installation guide, you should make sure to use a version later than 1.8.9.
Remember the version number it is set up to deploy, you will need to know that to install CLI tools!
- Select Deployment: Choose Minikube
- Graph Store: Select Cassandra (recommended for ease of use)
- Vector Store: Select Qdrant (recommended for ease of use)
- Chunker Settings:
- Type: Recursive
- LLM Model: Choose your preferred model as discussed above
- Output Tokens: 2048 is a safe default, 4096 works for most models, 8192 for the biggest models
- Customization: Leave defaults
- Finish Deployment: Click ‘Generate’ and then Download the deployment bundle
Unpack the configuration
The configuration builder will download a .zip file containing your deployment configuration which will be downloaded to your device in e.g. a Downloads directory. You need to find that zip file, and interact with it in a terminal. You can use the unzip command to list the contents of the ZIP file. There should be a resources.yaml file which is used to launch TrustGraph.
unzip -l deploy.zip
The output should look something like this:
Archive: deploy.zip
Length Date Time Name
--------- ---------- ----- ----
300102 2026-01-09 13:30 resources.yaml
--------- -------
300102 1 file
You should create a suitable directory for your work and move the YAML file there:
mkdir -p ~/trustgraph
cd ~/trustgraph
unzip ~/Downloads/deploy.zip .
Install CLI tools
You need to have access to TrustGraph client tools. In the terminal window you created above, install a virtual environment, and the TrustGraph CLI tools. Make sure the version number of the CLI tools matches the version you chose to build a configuration for earlier. i.e. replace 1.8.9 with the version you used earlier.
python3 -m venv env
. env/bin/activate
pip install trustgraph-cli==1.8.9
Deploy TrustGraph
Now you’re ready to deploy TrustGraph to your Minikube cluster.
Apply Kubernetes configuration
We’ll offer you 2 options for deploying the configuration.
- The simplest, in terms of commands, is to deploy the
resource.yamlfile, and then add the secret configuration. - The second, is to deploy the namespace, configure extra settings, and then deploy the application. This has the advantage that everything gets started with the resources it needs, so you’ll end up with a running system in quicker order.
So, option 1 is to run this command with the resources.yaml file you unpacked earlier:
kubectl apply -f resources.yaml
This creates all the necessary Kubernetes resources (deployments, services, configmaps, etc.) for TrustGraph. Some resources will fail to start until the configuration is complete, plus restart times.
Continue by deploying secrets below.
Option 2 is to deploy just the namespace. You need to have the yq utility installed for this command to work:
yq '.items[] | select(.kind == "Namespace")' resources.yaml | \
kubectl apply -f -
Configure LLM settings
Depending on which LLM you selected, you need to create a Kubernetes secret with your credentials or configuration.
Azure
There are 2 hosted model options for Azure:
- Machine Learning Services (MLS)
- Cognitive Services (CS)
TrustGraph’s Azure integration is for MLS. Azure OpenAI is for CS.
To use Azure, you need to know your model endpoint and the token granted for the endpoint.
Create the Kubernetes secret with your Azure credentials:
kubectl -n trustgraph create secret generic azure-credentials \
--from-literal="azure-endpoint=https://ENDPOINT.API.HOST.GOES.HERE/" \
--from-literal="azure-token=TOKEN-GOES-HERE"
AWS Bedrock
To use Bedrock, you need to have AWS credentials provisioned. The easiest way is to create an IAM user, and create credentials for this user. When you provision the user, you will be asked to give the user permissions. To allow Bedrock access, the AmazonBedrockFullAccess role should be added.
You would then provision credentials which would give you an access key ID and a secret access key. You should pick the identifier of an AWS region to connect to e.g. eu-west-2.
Note: You should be very careful with AWS cloud credentials provisioned this way: if lost or leaked this provides a malicious person access to the AWS resources you gave this user.
Create the Kubernetes secret with your AWS credentials:
kubectl -n trustgraph create secret generic bedrock-credentials \
--from-literal="aws-access-key-id=ID-KEY-HERE" \
--from-literal="aws-secret-access-key=TOKEN-GOES-HERE" \
--from-literal="aws-region=AWS-REGION-HERE"
Anthropic Claude
To use Anthropic’s Claude models directly, sign up for API access at console.anthropic.com. Create an API key from the dashboard.
Create the Kubernetes secret with your Claude API key:
kubectl -n trustgraph create secret generic claude-credentials \
--from-literal="claude-key=sk-ant-api03-xxxxx"
Cohere
To use Cohere’s models, sign up at cohere.com and create an API key from your dashboard.
Create the Kubernetes secret with your Cohere API key:
kubectl -n trustgraph create secret generic cohere-credentials \
--from-literal="cohere-key=your-cohere-api-key-here"
Google AI Studio
To use Google’s Gemini models via AI Studio, visit aistudio.google.com and generate an API key.
Create the Kubernetes secret with your Google AI Studio API key:
kubectl -n trustgraph create secret generic google-ai-studio-credentials \
--from-literal="google-ai-studio-key=your-api-key-here"
Llamafile / llama.cpp server
If running a llamafile or llama.cpp server locally, you need to configure the URL to point to your server. The URL must include the /v1 path.
If running on the same host as your Kubernetes cluster, use host.minikube.internal as the hostname (e.g., http://host.minikube.internal:7000/v1).
Create the Kubernetes secret with your Llamafile URL:
kubectl -n trustgraph create secret generic llamafile-credentials \
--from-literal="llamafile-url=http://host.minikube.internal:7000/v1"
LMStudio
If running LMStudio locally, you need to configure the URL to point to your LMStudio server. LMStudio typically runs on port 1234.
If running on the same host as your Kubernetes cluster, use host.minikube.internal as the hostname (e.g., http://host.minikube.internal:1234).
Create the Kubernetes secret with your LMStudio URL:
kubectl -n trustgraph create secret generic lmstudio-credentials \
--from-literal="lmstudio-url=http://host.minikube.internal:1234"
Mistral AI
To use Mistral’s API, sign up at console.mistral.ai and create an API key.
Create the Kubernetes secret with your Mistral API key:
kubectl -n trustgraph create secret generic mistral-credentials \
--from-literal="mistral-token=your-mistral-api-key-here"
Ollama
If running Ollama locally, you need to configure the URL to point to your Ollama server. Ollama typically runs on port 11434.
If running on the same host as your Kubernetes cluster, use host.minikube.internal as the hostname (e.g., http://host.minikube.internal:11434).
Create the Kubernetes secret with your Ollama host URL:
kubectl -n trustgraph create secret generic ollama-credentials \
--from-literal="ollama-host=http://host.minikube.internal:11434"
OpenAI
To use OpenAI’s API, sign up at platform.openai.com and create an API key.
Create the Kubernetes secret with your OpenAI API key:
kubectl -n trustgraph create secret generic openai-credentials \
--from-literal="openai-token=your-openai-api-key-here"
If using an alternative OpenAI-compatible API, you can also specify a base URL:
kubectl -n trustgraph create secret generic openai-credentials \
--from-literal="openai-token=your-openai-api-key-here" \
--from-literal="openai-base-url=http://your-server-host:8000/v1"
Google Cloud VertexAI
To use Google Cloud VertexAI, you need to create a service account with appropriate permissions and download its credentials file.
- In Google Cloud Console, create a service account
- Grant the service account permissions to invoke VertexAI models (e.g.,
Vertex AI Userrole - use minimal permissions, not admin roles) - Create and download a JSON key file for the service account
- Save the key file as
vertexai/private.jsonin your deployment directory
Important: Service account credentials provide access to your Google Cloud resources. Never commit private.json to version control. Use minimal permissions - grant only what’s needed for VertexAI model invocation, not administrator roles.
Create the Kubernetes secret from the credentials file:
kubectl -n trustgraph create secret generic vertexai-credentials \
--from-file=private.json=vertexai/private.json
vLLM
If running vLLM locally, you need to configure the URL to point to your vLLM server. The URL should include the /v1 path.
If running on the same host as your Kubernetes cluster, use host.minikube.internal as the hostname (e.g., http://host.minikube.internal:8000/v1).
Create the Kubernetes secret with your vLLM URL:
kubectl -n trustgraph create secret generic vllm-credentials \
--from-literal="vllm-url=http://host.minikube.internal:8000/v1"
Configure security settings
First, create the security secrets. For this local deployment, we set these to empty strings to disable authentication:
kubectl -n trustgraph create secret generic gateway-secret \
--from-literal=gateway-secret=""
kubectl -n trustgraph create secret generic mcp-server-secret \
--from-literal=mcp-server-secret=""
The mcp-server-secret protects the MCP server with a secret but is not fully implemented yet. The gateway-secret provides single-secret protection for the gateway API, which does not currently support comprehensive API security. For a local non-networked deployment, it is safe to disable authentication by setting these to empty strings.
Finish configuration
If you went with option 1, there is no more configuration to do, but you may have to wait a while. Parts of the system will have started, realised the configuration wasn’t present, and backed off for a while.
If you want with option 2, you finish by deploying the rest of the system:
kubectl apply -f resources.yaml
At this point you should have all the necessary Kubernetes resources (deployments, services, configmaps, etc.) for TrustGraph.
At this point, you should wait until resources have started before continuing. This shows the running workloads:
kubectl -n trustgraph get pods
The result for a working system will look something like this. Pods should be running. We run 3 initialisation containers which exit once their work is done, so it’s OK for those to be in a failed state.
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
agent-manager-74fbb8b64-nzlwb 1/1 Running 0 67m
api-gateway-b6848c6bb-nqtdm 1/1 Running 0 67m
bookie-5b8f57c985-d665l 1/1 Running 1 (63m ago) 67m
cassandra-6765fff974-pbh65 1/1 Running 0 67m
chunker-5449fddbf4-zgc5s 1/1 Running 0 67m
config-svc-7ff5684cbb-j2rbl 1/1 Running 0 67m
ddg-mcp-server-5b6d456cd9-lttts 1/1 Running 0 67m
document-embeddings-6f57c977b8-5ksqt 1/1 Running 0 67m
document-rag-67857f95b5-n8klg 1/1 Running 0 67m
embeddings-8688f5875b-8wrxb 1/1 Running 0 67m
garage-69bbc995bb-ggsbd 1/1 Running 0 67m
garage-init-5c59cdc77f-hz46c 0/1 CrashLoopBackOff 17 (2m7s ago) 67m
grafana-795dcfc9bf-ctsxv 1/1 Running 0 67m
graph-embeddings-7b75fd6845-hrh9v 1/1 Running 0 67m
graph-rag-7f4bc95f7-q4jpl 1/1 Running 0 67m
init-trustgraph-7798b9d4f8-qzdgt 0/1 CrashLoopBackOff 17 (57s ago) 67m
kg-extract-agent-7f6f754fb9-d5fh5 1/1 Running 0 67m
kg-extract-definitions-54b454d784-2pkc2 1/1 Running 0 67m
kg-extract-objects-5cdbdfdcc4-j885c 1/1 Running 0 67m
kg-extract-ontology-7557fd7dc-2gf6j 1/1 Running 0 67m
kg-extract-relationships-7cbf57d9b7-qnv47 1/1 Running 0 67m
kg-manager-678c57d885-ptv9m 1/1 Running 0 67m
kg-store-6bc8b9c9b7-5chdr 1/1 Running 0 67m
librarian-75c8f6d7fb-98rkc 1/1 Running 0 67m
loki-8d5b86fb5-s9k4d 1/1 Running 0 67m
mcp-server-56bd6c4d6-788nw 1/1 Running 0 67m
mcp-tool-698f4b898b-ggm6l 1/1 Running 0 67m
metering-57d9fccdd-m45vp 1/1 Running 0 67m
metering-rag-5b9f8d5495-cnxsv 1/1 Running 0 67m
nlp-query-9666cf9b6-wmzwv 1/1 Running 0 67m
pdf-decoder-69fd89776b-2cfpj 1/1 Running 0 67m
prometheus-54995cff86-dc58n 1/1 Running 0 67m
prompt-899b97d7d-5rd6m 1/1 Running 0 67m
prompt-rag-5dc4f4b89b-qqvw7 1/1 Running 0 67m
pulsar-d85499879-x92qv 1/1 Running 0 67m
pulsar-init-6cd9ff4fbb-m5j7t 0/1 CrashLoopBackOff 16 (22s ago) 67m
qdrant-58497bc84-rm9gm 1/1 Running 0 67m
query-doc-embeddings-5f6985ffd6-5qh9s 1/1 Running 0 67m
query-graph-embeddings-588bd9779-7ddbb 1/1 Running 0 67m
query-objects-bcd6fd894-w9bm7 1/1 Running 0 67m
query-triples-55549dc477-bdcgj 1/1 Running 0 67m
store-doc-embeddings-dbf4b7c69-w998d 1/1 Running 0 67m
store-graph-embeddings-7885698676-vf422 1/1 Running 0 67m
store-objects-655bf8b975-jcg2r 1/1 Running 0 67m
store-triples-7c59c67f6-d8hbs 1/1 Running 0 67m
structured-diag-86c58cd45b-54w8m 1/1 Running 0 67m
structured-query-67fdff6967-7kljs 1/1 Running 0 67m
text-completion-58ccf95586-6gkff 1/1 Running 0 67m
text-completion-rag-75fc684f58-82jjm 1/1 Running 0 67m
workbench-ui-5fc6d59899-8rczf 1/1 Running 0 67m
zookeeper-66c484c7d5-67578 1/1 Running 0 67m
Launch LoadBalancer
Open a separate terminal window and run:
minikube tunnel
This command finds all the services running on Kubernetes and exposes them on a service address. The output tells you the service address:
Status:
machine: minikube
pid: 465861
route: 10.96.0.0/12 -> 192.168.39.34
minikube: Running
services: [agent-manager, api-gateway, bookie, cassandra, chunker, config-svc, ddg-mcp-server, document-embeddings, document-rag, embeddings, garage, grafana, graph-embeddings, graph-rag, kg-extract-agent, kg-extract-definitions, kg-extract-objects, kg-extract-ontology, kg-extract-relationships, kg-manager, kg-store, librarian, loki, mcp-server, mcp-tool, metering, metering-rag, nlp-query, pdf-decoder, prometheus, prompt, prompt-rag, pulsar, qdrant, query-doc-embeddings, query-graph-embeddings, query-objects, query-triples, store-doc-embeddings, store-graph-embeddings, store-objects, store-triples, structured-diag, structured-query, text-completion, text-completion-rag, workbench-ui, zookeeper]
errors:
minikube: no errors
router: no errors
loadbalancer emulator: no errors
In this case, 192.168.39.34 is the address at which you can access all Kubernetes services. This is an address which is internal to your system and will not be accessible outside of your host.
Keep this terminal window open. The LoadBalancer must remain running for cluster communications to be accessible from ‘outside’ the cluster.
Verify startup
It can take around 2 - 3 minutes for all services to stabilize. Services like Pulsar and Cassandra need time to initialize properly. There is a utility which runs a series of checks to verify the system as it starts and reports when the system is working successfully.
Note: TrustGraph commands attempt to connect to services at localhost by default, and the only way to communicate with TrustGraph services on Minikube is to use the tunnel address you created earlier. So, commands need to be told where to communicate with TrustGraph services.
To verify the working system, use the IP address of the minikube tunnel:
tg-verify-system-status \
--api-url http://192.168.39.34:8088 \
--pulsar-url http://192.168.39.34:8080 \
--ui-url http://192.168.39.34:8888
If everything is working, the output looks something like this:
============================================================
TrustGraph System Status Verification
============================================================
Phase 1: Infrastructure
------------------------------------------------------------
[00:00] ⏳ Checking Pulsar...
[00:03] ⏳ Checking Pulsar... (attempt 2)
[00:03] ✓ Pulsar: Pulsar healthy (0 cluster(s))
[00:03] ⏳ Checking API Gateway...
[00:03] ✓ API Gateway: API Gateway is responding
Phase 2: Core Services
------------------------------------------------------------
[00:03] ⏳ Checking Processors...
[00:03] ✓ Processors: Found 34 processors (≥ 15)
[00:03] ⏳ Checking Flow Classes...
[00:06] ⏳ Checking Flow Classes... (attempt 2)
[00:09] ⏳ Checking Flow Classes... (attempt 3)
[00:22] ⏳ Checking Flow Classes... (attempt 4)
[00:35] ⏳ Checking Flow Classes... (attempt 5)
[00:38] ⏳ Checking Flow Classes... (attempt 6)
[00:38] ✓ Flow Classes: Found 9 flow blueprint(es)
[00:38] ⏳ Checking Flows...
[00:38] ✓ Flows: Flow manager responding (1 flow(s))
[00:38] ⏳ Checking Prompts...
[00:38] ✓ Prompts: Found 16 prompt(s)
Phase 3: Data Services
------------------------------------------------------------
[00:38] ⏳ Checking Library...
[00:38] ✓ Library: Library responding (0 document(s))
Phase 4: User Interface
------------------------------------------------------------
[00:38] ⏳ Checking Workbench UI...
[00:38] ✓ Workbench UI: Workbench UI is responding
============================================================
Summary
============================================================
Checks passed: 8/8
Checks failed: 0/8
Total time: 00:38
✓ System is healthy!
The Checks failed line is the most interesting and is hopefully zero. If you are having issues, look at the troubleshooting section later.
If everything appears to be working, the following parts of the deployment guide are a whistle-stop tour through various parts of the system.
Test LLM access
This tests that LLM access works by accessing the gateway through the LLM tunnel. This uses the tunnel address discovered above:
tg-invoke-llm -u http://192.168.39.34:8088 'Be helpful' 'What is 2 + 2?'
You should see output like…
2 + 2 = 4
Load sample documents
There is a utility which loads a small set of sample documents into the library. This does not initiate processing, but gives you a set of documents to test with. Again, this uses the tunnel address:
tg-load-sample-documents -u http://192.168.39.34:8088
This downloads documents from the internet and caches them in a local directory, so that the load is quicker if you need to do it again. The download can take a little time to run.
Workbench
TrustGraph is bundled with a simple web interface which exercises most of the functionality.
Access the TrustGraph workbench at the appropriate URL, which, using the IP address above, would like:
http://192.168.39.34:8888
By default, there are no credentials.
You should be able to navigate to the Flows tab, and see a single default flow running. The guide will return to the workbench to load a document.
Monitoring dashboard
Access Grafana at the appropriate URL, which, using the IP address above looks like this:
http://192.168.39.34:3000
Default credentials:
- Username:
admin - Password:
admin
All TrustGraph components collect metrics using Prometheus and make these available using this Grafana workbench. The Grafana deployment is configured with 2 dashboards, the first is an Overview metrics dashboard which shows processing metrics. For a newly launched system, the metrics won’t be particularly interesting.
There is also a Logs dashboard which shows collated TrustGraph container logs.
Check the LLM is working
Back in the workbench, select the Assistant tab.
In the top line next to the Assistant word, change the mode to Basic LLM.
Enter a question in the prompt box at the bottom of the tab and press Send. If everything works, after a short period you should see a response to your query.
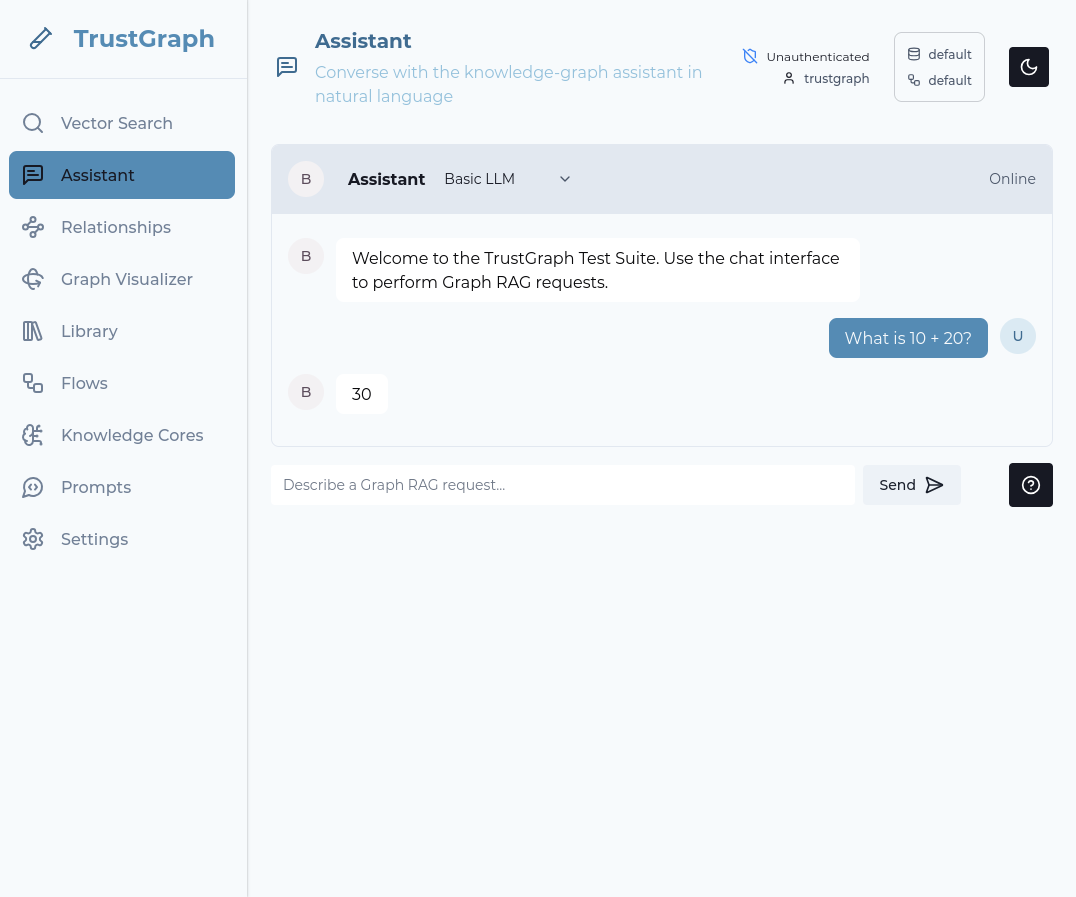
If LLM interactions are not working, check the Grafana logs dashboard for errors in the text-completion service.
Working with a document
Load a document
Back in the workbench:
- Navigate to the Library page
- In the upper right-hand corner, there is a dark/light mode widget. To its left is a selector widget. Ensure the top and bottom lines say “default”. If not, click on the widget and change.
- On the library tab, select a document (e.g., “Beyond State Vigilance”)
- Click Submit on the action bar
- Choose a processing flow (use Default processing flow)
- Click Submit to process
Beyond State Vigilance is a relatively short document, so it’s a good one to start with.
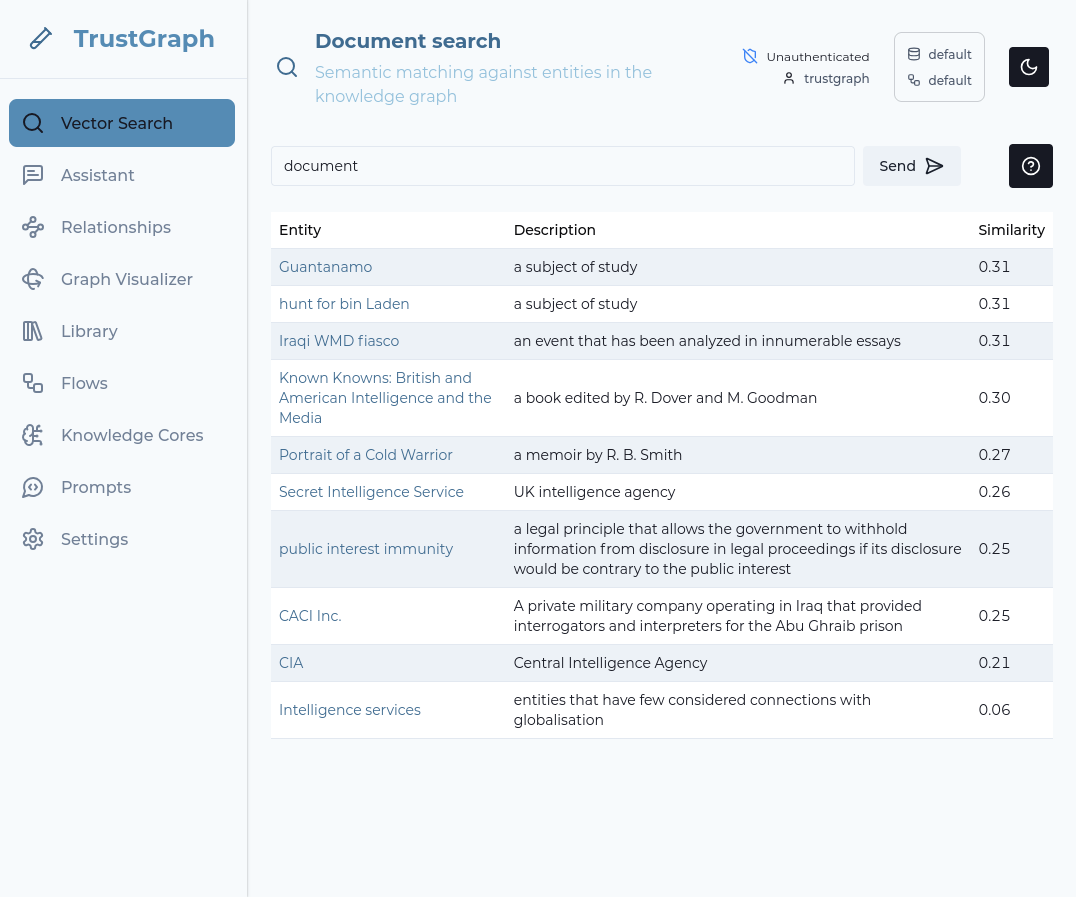
Use Vector search
Select the Vector Search tab. Enter a string (e.g., “document”) in the search bar and hit RETURN. The search term doesn’t matter a great deal. If information has started to load, you should see some search results.
The vector search attempts to find up to 10 terms which are the closest matches for your search term. It does this even if the search terms are not a strong match, so this is a simple way to observe whether data has loaded.
Look at knowledge graph
Click on one of the Vector Search result terms on the left-hand side. This shows relationships in the graph from the knowledge graph linking to that term.
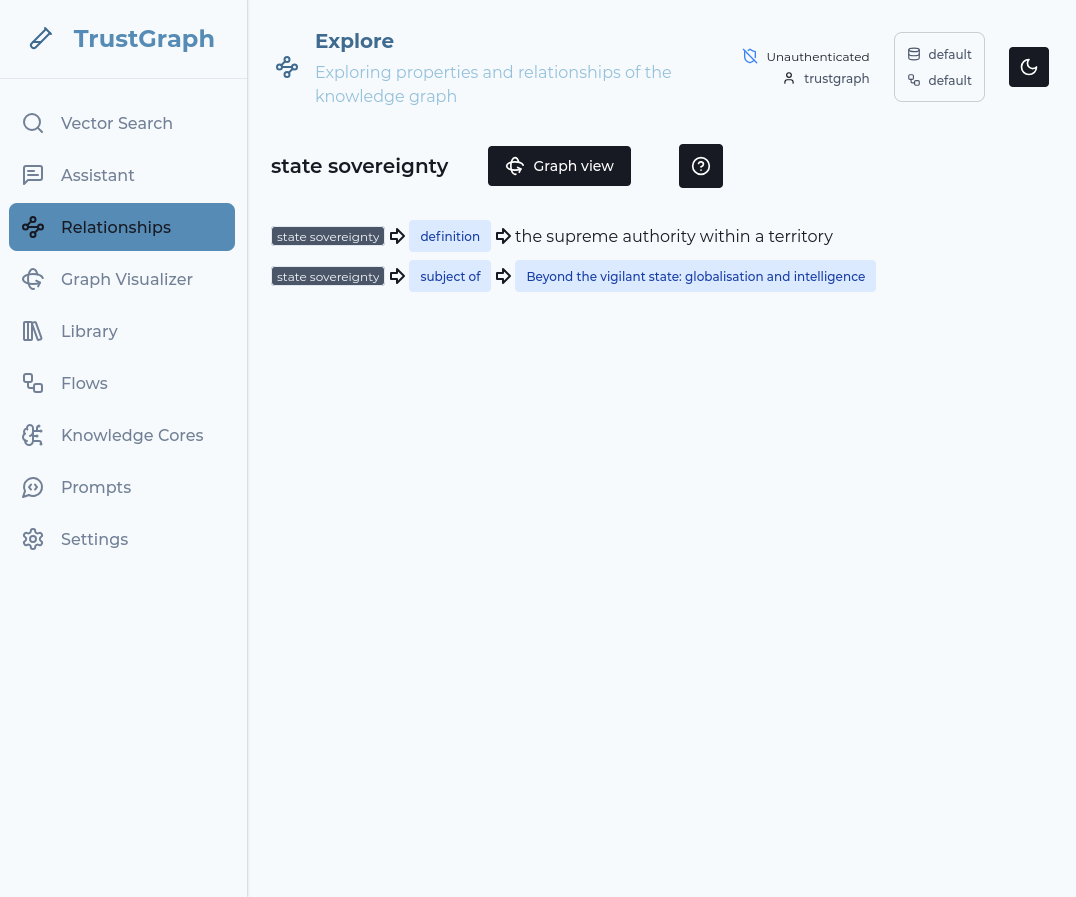
You can then click on the Graph view button to go to a 3D view of the discovered relationships.
Query with Graph RAG
- Navigate to Assistant tab
- Change the Assistant mode to GraphRAG
- Enter your question (e.g., “What is this document about?”)
- You will see the answer to your question after a short period
Troubleshooting
Service Failure
Run out of memory
Diagnosis:
Check which pods are running. Init containers (names ending in -init) should show Completed - this is normal. Other pods should be running.
# Show all pods
kubectl -n trustgraph get pods
# Find OOM-killed pods (look for OOMKilled status)
kubectl -n trustgraph get pods | grep -i oom
# Inspect a failed pod for details
kubectl -n trustgraph describe pod <pod-name> | grep -A 5 "OOMKilled\|Error"
Look for "OOMKilled": true or error messages in the describe output.
Resolution:
- Increase memory allocation when starting Minikube:
minikube stop minikube start --cpus=9 --memory=16384 - Alternative: Run on a machine with more available memory (20GB+ recommended)
Hitting major CPU resource limits
Diagnosis:
System is very slow to start, taking several minutes to become available. Operations are sluggish. Check CPU load:
# Check node resources
kubectl -n trustgraph top nodes
# Check pod resource usage
kubectl -n trustgraph top pods
If CPU usage remains very high for an extended period during startup and operations, this indicates insufficient CPU resources.
Resolution:
Increase CPU allocation when starting Minikube:
minikube stop
minikube start --cpus=12 --memory=11264
TrustGraph requires 9 CPUs minimum, but more cores will improve performance significantly.
Image Pull Issues
Diagnosis:
Check for pods in ImagePullBackOff or ErrImagePull status:
# Check pod status
kubectl -n trustgraph get pods
# View pod events for image pull errors
kubectl -n trustgraph get events | grep -i "pull\|image"
# Describe a specific pod
kubectl -n trustgraph describe pod <pod-name>
Look for errors mentioning image pull failures, authentication issues, or network problems.
Resolution:
- Network connectivity: Ensure Minikube has internet access
- Image registry access: Verify you can reach the container registry
- Authentication: If using a private registry, ensure credentials are configured
- Retry: Sometimes transient network issues resolve themselves:
kubectl -n trustgraph delete pod <pod-name> # Kubernetes will recreate the pod
LoadBalancer Not Starting
Diagnosis:
The minikube tunnel command fails or services remain in Pending state:
# Check service status
kubectl -n trustgraph get services
# Check Minikube status
minikube status
Look for services with EXTERNAL-IP showing <pending>.
Resolution:
- Ensure
minikube tunnelis running in a separate terminal window - The tunnel command requires sudo/administrator privileges
- Check Minikube driver is working:
minikube config view - Restart the tunnel:
# Stop existing tunnel (Ctrl+C) minikube tunnel
Application error
Diagnosis:
Find failed pods and examine their logs:
# Show all pods with status
kubectl -n trustgraph get pods
# View logs for a specific pod
kubectl -n trustgraph logs <pod-name>
# Follow logs in real-time
kubectl -n trustgraph logs -f <pod-name>
# View logs for a specific container in a multi-container pod
kubectl -n trustgraph logs <pod-name> -c <container-name>
Alternatively, view aggregated logs in the Grafana dashboard if available.
Resolution:
Resolution depends on the specific error message. Common issues include configuration errors, missing environment variables, missing secrets, or service dependencies not being ready.
LLM Failure
LLM configuration error
Diagnosis:
The system appears to be running but LLM connectivity is not working. Test LLM connectivity:
tg-invoke-llm '' 'What is 2+2'
A long timeout or error indicates LLM configuration issues. Check the logs:
# Check text-completion service logs
kubectl -n trustgraph logs -l app=text-completion
Look for errors indicating LLM connection failures.
Resolution:
Review the LLM configuration settings in the Configure LLM settings section. Common issues include:
- Missing or incorrect API keys
- Wrong endpoint URLs
- Missing
/v1suffix for self-hosted models - Incorrect
host.minikube.internalhostname for local services - Secrets not created properly in Kubernetes
Verify your secrets are created:
kubectl -n trustgraph get secrets
Locally-hosted LLM connectivity error
Diagnosis:
Check the logs for connectivity errors:
kubectl -n trustgraph logs -l app=text-completion
Look for errors indicating connection refused, timeouts, or unreachable hosts when attempting to connect to your LLM service.
Resolution:
Review your network connectivity and addressing configuration:
- Verify your LLM service is running and accessible from your host
- Check the URL configuration for your LLM (environment variables)
- For services on the same host, ensure you’re using
host.minikube.internalas the hostname - Verify the correct port number
- Ensure URLs include
/v1suffix where required - Test connectivity from within Minikube:
kubectl run -it --rm debug --image=curlimages/curl --restart=Never -- \ curl -v http://host.minikube.internal:11434
See also:
Kubernetes-Specific Issues
Pods stuck in Pending state
Diagnosis:
# Check pod status
kubectl -n trustgraph get pods | grep Pending
# Describe a pending pod
kubectl -n trustgraph describe pod <pod-name>
Look for scheduling failures, resource constraints, or node conditions.
Resolution:
- Insufficient resources: Increase Minikube resources (see above)
- PersistentVolume issues: Check PV/PVC status:
kubectl -n trustgraph get pv,pvc - Node issues: Check node status:
kubectl describe node minikube
Pods in CrashLoopBackOff
Diagnosis:
# Find crashing pods
kubectl -n trustgraph get pods | grep CrashLoopBackOff
# View logs from crashed container
kubectl -n trustgraph logs <pod-name> --previous
Resolution:
Check the previous logs to identify why the container is crashing. Common causes:
- Application errors (fix the configuration)
- Missing dependencies (ensure all required services are running)
- Incorrect environment variables or secrets
- Resource limits too low (increase in deployment configuration)
Shutting down
Clean shutdown
Once you have finished with your system, you can close it down.
minikube delete
Next Steps
- Guides: See Guides for things you can do with your running TrustGraph
- Production Kubernetes: Scale to full Kubernetes clusters
- Cloud Deployment: Explore AWS EKS, GCP GKE, or Azure AKS for managed Kubernetes