Amazon Web Services (RKE) Deployment
Production-ready RKE2 Kubernetes cluster on AWS with Bedrock AI integration
Advanced
2 - 5 hr
- AWS account with appropriate permissions (see below for setup)
- AWS CLI installed and configured
- Pulumi installed locally
- kubectl command-line tool
- Python 3.11+ for CLI tools
- SSH key pair for EC2 access
- Basic command-line and Kubernetes familiarity
Deploy a production-ready TrustGraph environment on AWS using RKE2 Kubernetes with AWS Bedrock integration and security hardening.
Overview
This guide walks you through deploying TrustGraph on Amazon Web Services using RKE2 (Rancher Kubernetes Engine 2) via Pulumi (Infrastructure as Code). The deployment automatically provisions a production-ready, security-hardened Kubernetes cluster integrated with AWS Bedrock for LLM capabilities.
Pulumi is an open-source Infrastructure as Code tool that uses general-purpose programming languages (TypeScript/JavaScript in this case) to define cloud infrastructure. Unlike manual deployments, Pulumi provides:
- Reproducible, version-controlled infrastructure
- Testable and retryable deployments
- Automatic resource dependency management
- Simple rollback capabilities
RKE2 (Rancher Kubernetes Engine 2) is a fully conformant Kubernetes distribution that focuses on security and compliance:
- FIPS 140-2 compliance ready
- CIS Kubernetes Benchmark hardened
- Simplified operations with embedded etcd
- Government and enterprise security requirements
Once deployed, you’ll have a complete TrustGraph stack running on AWS infrastructure with:
- RKE2 Kubernetes cluster (3-node setup, configurable)
- AWS Bedrock integration (Claude 3.5 Haiku default)
- EBS CSI driver for persistent storage
- Complete monitoring with Grafana and Prometheus
- Web workbench for document processing and Graph RAG
- Secure IAM roles and policies
Why AWS RKE2 for TrustGraph?
AWS with RKE2 offers unique advantages for security-focused organizations:
- Security Hardening: RKE2 is CIS Benchmark hardened and FIPS 140-2 ready
- AWS Bedrock: Native access to Claude, Mistral, and other frontier models
- Government Ready: Meets stringent government and enterprise security requirements
- AWS Integration: Seamless integration with AWS services (EBS, IAM, VPC, etc.)
- Global Infrastructure: Deploy across AWS’s global network of regions
Ideal for organizations requiring high security standards and compliance.
Getting ready
AWS Account
You’ll need an AWS account with appropriate permissions. If you don’t have one:
- Sign up at https://aws.amazon.com/
- Complete account verification
- Set up billing
- AWS Free Tier includes 750 hours/month of EC2 for 12 months
AWS Permissions Required
Your AWS user/role needs permissions for:
- EC2 (instances, VPC, security groups, key pairs)
- IAM (roles, policies, instance profiles)
- EBS (volumes, snapshots)
- Bedrock (model access)
Install AWS CLI
Install the AWS command-line tool:
Linux
curl "https://awscli.amazonaws.com/awscli-exe-linux-x86_64.zip" -o "awscliv2.zip"
unzip awscliv2.zip
sudo ./aws/install
MacOS
curl "https://awscli.amazonaws.com/AWSCLIV2.pkg" -o "AWSCLIV2.pkg"
sudo installer -pkg AWSCLIV2.pkg -target /
Windows
Download the installer from aws.amazon.com/cli
Verify installation:
aws --version
Configure AWS Credentials
Configure your AWS credentials:
aws configure
You’ll be prompted for:
- AWS Access Key ID
- AWS Secret Access Key
- Default region (e.g.,
us-west-2) - Default output format (recommend
json)
Verify configuration:
aws sts get-caller-identity
Enable AWS Bedrock Models
AWS Bedrock requires explicit model access enablement:
- Navigate to the AWS Bedrock Console
- Select your deployment region
- Go to Model access in the left navigation
- Click Manage model access
- Enable access to:
- Anthropic Claude 3.5 Haiku (recommended default)
- Mistral Nemo Instruct (optional alternative)
- Any other models you want to use
- Submit request (usually approved immediately for most models)
Model access must be enabled in the same region where you’ll deploy TrustGraph.
Create SSH Key Pair
Create an SSH key pair for EC2 instance access:
aws ec2 create-key-pair \
--key-name trustgraph-key \
--query 'KeyMaterial' \
--output text > ~/.ssh/trustgraph-key.pem
chmod 400 ~/.ssh/trustgraph-key.pem
Python
You need Python 3.11 or later installed for the TrustGraph CLI tools.
Check your Python version
python3 --version
If you need to install or upgrade Python, visit python.org.
Pulumi
Install Pulumi on your local machine:
Linux
curl -fsSL https://get.pulumi.com | sh
MacOS
brew install pulumi/tap/pulumi
Windows
Download the installer from pulumi.com.
Verify installation:
pulumi version
Full installation details are at pulumi.com.
kubectl
Install kubectl to manage your Kubernetes cluster:
- Linux: Install kubectl on Linux
- MacOS:
brew install kubectl - Windows: Install kubectl on Windows
Verify installation:
kubectl version --client
Node.js
The Pulumi deployment code uses TypeScript/JavaScript, so you’ll need Node.js installed:
- Download: nodejs.org (LTS version recommended)
- Linux:
sudo apt install nodejs npm(Ubuntu/Debian) orsudo dnf install nodejs(Fedora) - MacOS:
brew install node
Verify installation:
node --version
npm --version
Prepare the deployment
Get the Pulumi code
Clone the TrustGraph AWS RKE Pulumi repository:
git clone https://github.com/trustgraph-ai/pulumi-trustgraph-aws-rke.git
cd pulumi-trustgraph-aws-rke/pulumi
Install dependencies
Install the Node.js dependencies for the Pulumi project:
npm install
Configure Pulumi state
You need to tell Pulumi which state to use. You can store this in an S3 bucket, but for experimentation, you can just use local state:
pulumi login --local
When storing secrets in the Pulumi state, pulumi uses a secret passphrase to encrypt secrets. When using Pulumi in a production or shared environment you would have to evaluate the security arrangements around secrets.
We’re just going to set this to the empty string, assuming that no encryption is fine for a development deploy.
export PULUMI_CONFIG_PASSPHRASE=
Create a Pulumi stack
Initialize a new Pulumi stack for your deployment:
pulumi stack init dev
You can use any name instead of dev - this helps you manage multiple deployments (dev, staging, prod, etc.).
Configure the stack
Apply settings for AWS region, environment, and infrastructure:
pulumi config set aws:region us-west-2
pulumi config set environment prod
pulumi config set keyName trustgraph-key
pulumi config set instanceType t3a.xlarge
pulumi config set nodeCount 3
Available AWS regions include:
us-east-1(N. Virginia)us-west-2(Oregon)eu-west-1(Ireland)eu-central-1(Frankfurt)ap-southeast-1(Singapore)ap-northeast-1(Tokyo)
Refer to AWS Regions for a complete list.
Configure AWS Bedrock
Set the Bedrock model to use:
pulumi config set bedrockModel anthropic.claude-3-5-haiku-20241022-v1:0
Available Bedrock models include:
anthropic.claude-3-5-haiku-20241022-v1:0(fast, cost-effective)anthropic.claude-3-5-sonnet-20241022-v2:0(balanced performance)mistral.mistral-nemo-instruct-2407-v1:0(open source)
Refer to the repository’s README for more model options.
Configure VPC Settings (Optional)
Customize network configuration if needed:
pulumi config set vpcCidr 172.38.0.0/16
pulumi config set subnetCidr 172.38.1.0/24
Deploy with Pulumi
Preview the deployment
Before deploying, preview what Pulumi will create:
pulumi preview
This shows all the resources that will be created:
- VPC with custom CIDR block
- Subnet and Internet Gateway
- Security groups for RKE2 cluster
- IAM roles and policies (with Bedrock permissions)
- EC2 instances for Kubernetes nodes
- EBS volumes for persistent storage
- RKE2 cluster configuration
- EBS CSI driver deployment
- TrustGraph deployments, services, and config maps
Review the output to ensure everything looks correct.
Deploy the infrastructure
Deploy the complete TrustGraph stack:
pulumi up
Pulumi will ask for confirmation before proceeding. Type yes to continue.
The deployment typically takes 12 - 18 minutes and progresses through these stages:
- Creating AWS infrastructure (3-5 minutes)
- Creates VPC, subnet, and networking
- Provisions security groups
- Creates IAM roles and policies
- Launching EC2 instances (2-3 minutes)
- Launches RKE2 server node
- Launches RKE2 agent nodes
- Attaches EBS volumes
- Installing RKE2 (5-7 minutes)
- Installs RKE2 on server node
- Installs RKE2 on agent nodes
- Forms Kubernetes cluster
- Deploying TrustGraph (4-6 minutes)
- Installs EBS CSI driver
- Applies Kubernetes manifests
- Deploys all TrustGraph services
- Starts pods and initializes services
You’ll see output showing the creation progress of all resources.
Post-deployment initialization: After all pods show “Running” status, wait an additional 30 seconds for internal service initialization to complete before running verification commands.
Configure and verify kubectl access
After deployment completes, a kubeconfig file is created for cluster access:
export KUBECONFIG=$(pwd)/kubeconfig.yaml
Verify access:
kubectl get nodes
You should see your RKE2 nodes listed as Ready.
Check pod status
Verify that all pods are running:
kubectl -n trustgraph get pods
You should see output similar to this (pod names will have different random suffixes):
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
agent-manager-74fbb8b64-nzlwb 1/1 Running 0 5m
api-gateway-b6848c6bb-nqtdm 1/1 Running 0 5m
cassandra-6765fff974-pbh65 1/1 Running 0 5m
pulsar-d85499879-x92qv 1/1 Running 0 5m
text-completion-58ccf95586-6gkff 1/1 Running 0 5m
workbench-ui-5fc6d59899-8rczf 1/1 Running 0 5m
...
All pods should show Running status. Some init pods (names ending in -init) may fail or be shown Completed status - this is normal, their job is to initialise cluster resources and then exit.
Access services via port-forwarding
Since the Kubernetes cluster is running on Scaleway, you’ll need to set up port-forwarding to access TrustGraph services from your local machine.
Open three separate terminal windows and run these commands (keep them running):
Terminal 1 - API Gateway:
export KUBECONFIG=$(pwd)/kubeconfig.yaml
kubectl -n trustgraph port-forward svc/api-gateway 8088:8088
Terminal 2 - Workbench UI:
export KUBECONFIG=$(pwd)/kubeconfig.yaml
kubectl -n trustgraph port-forward svc/workbench-ui 8888:8888
Terminal 3 - Grafana:
export KUBECONFIG=$(pwd)/kubeconfig.yaml
kubectl -n trustgraph port-forward svc/grafana 3000:3000
With these port-forwards running, you can access:
- TrustGraph API: http://localhost:8088
- Web Workbench: http://localhost:8888
- Grafana Monitoring: http://localhost:3000
Keep these terminal windows open while you’re working with TrustGraph. If you close them, you’ll lose access to the services.
Install CLI tools
Now install the TrustGraph command-line tools. These tools help you interact with TrustGraph, load documents, and verify the system.
Create a Python virtual environment and install the CLI:
python3 -m venv env
source env/bin/activate # On Windows: env\Scripts\activate
pip install trustgraph-cli
Startup period
It can take 2-3 minutes for all services to stabilize after deployment. Services like Pulsar and Cassandra need time to initialize properly. Additionally, wait 30 seconds after pods show “Running” status for internal initialization.
Verify system health
tg-verify-system-status
If everything is working, the output looks something like this:
============================================================
TrustGraph System Status Verification
============================================================
Phase 1: Infrastructure
------------------------------------------------------------
[00:00] ⏳ Checking Pulsar...
[00:03] ⏳ Checking Pulsar... (attempt 2)
[00:03] ✓ Pulsar: Pulsar healthy (0 cluster(s))
[00:03] ⏳ Checking API Gateway...
[00:03] ✓ API Gateway: API Gateway is responding
Phase 2: Core Services
------------------------------------------------------------
[00:03] ⏳ Checking Processors...
[00:03] ✓ Processors: Found 34 processors (≥ 15)
[00:03] ⏳ Checking Flow Classes...
[00:06] ⏳ Checking Flow Classes... (attempt 2)
[00:09] ⏳ Checking Flow Classes... (attempt 3)
[00:22] ⏳ Checking Flow Classes... (attempt 4)
[00:35] ⏳ Checking Flow Classes... (attempt 5)
[00:38] ⏳ Checking Flow Classes... (attempt 6)
[00:38] ✓ Flow Classes: Found 9 flow class(es)
[00:38] ⏳ Checking Flows...
[00:38] ✓ Flows: Flow manager responding (1 flow(s))
[00:38] ⏳ Checking Prompts...
[00:38] ✓ Prompts: Found 16 prompt(s)
Phase 3: Data Services
------------------------------------------------------------
[00:38] ⏳ Checking Library...
[00:38] ✓ Library: Library responding (0 document(s))
Phase 4: User Interface
------------------------------------------------------------
[00:38] ⏳ Checking Workbench UI...
[00:38] ✓ Workbench UI: Workbench UI is responding
============================================================
Summary
============================================================
Checks passed: 8/8
Checks failed: 0/8
Total time: 00:38
✓ System is healthy!
The Checks failed line is the most interesting and is hopefully zero. If you are having issues, look at the troubleshooting section later.
If everything appears to be working, the following parts of the deployment guide are a whistle-stop tour through various parts of the system.
Test LLM access
Test that AWS Bedrock integration is working by invoking the LLM through the gateway:
tg-invoke-llm 'Be helpful' 'What is 2 + 2?'
You should see output like:
2 + 2 = 4
This confirms that TrustGraph can successfully communicate with AWS Bedrock.
Load sample documents
Load a small set of sample documents into the library for testing:
tg-load-sample-documents
This downloads documents from the internet and caches them locally. The download can take a little time to run.
Workbench
TrustGraph includes a web interface for document processing and Graph RAG.
Access the TrustGraph workbench at http://localhost:8888 (requires port-forwarding to be running).
By default, there are no credentials.
You should be able to navigate to the Flows tab and see a single default flow running. The guide will return to the workbench to load a document.
Monitoring dashboard
Access Grafana monitoring at http://localhost:3000 (requires port-forwarding to be running).
Default credentials:
- Username:
admin - Password:
admin
All TrustGraph components collect metrics using Prometheus and make these available using this Grafana workbench. The Grafana deployment is configured with 2 dashboards:
- Overview metrics dashboard: Shows processing metrics
- Logs dashboard: Shows collated TrustGraph container logs
For a newly launched system, the metrics won’t be particularly interesting yet.
Check the LLM is working
Back in the workbench, select the Assistant tab.
In the top line next to the Assistant word, change the mode to Basic LLM.
Enter a question in the prompt box at the bottom of the tab and press Send. If everything works, after a short period you should see a response to your query.
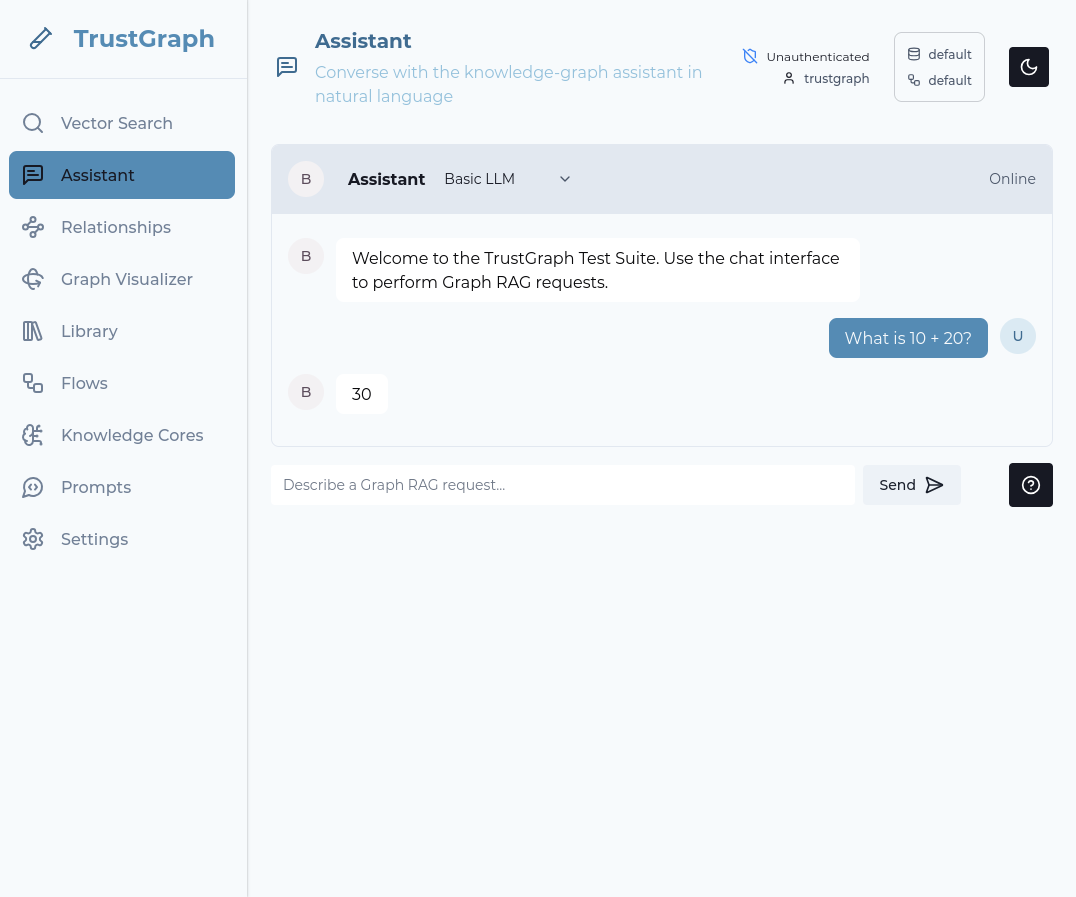
If LLM interactions are not working, check the Grafana logs dashboard for errors in the text-completion service.
Working with a document
Load a document
Back in the workbench:
- Navigate to the Library page
- In the upper right-hand corner, there is a dark/light mode widget. To its left is a selector widget. Ensure the top and bottom lines say “default”. If not, click on the widget and change.
- On the library tab, select a document (e.g., “Beyond State Vigilance”)
- Click Submit on the action bar
- Choose a processing flow (use Default processing flow)
- Click Submit to process
Beyond State Vigilance is a relatively short document, so it’s a good one to start with.
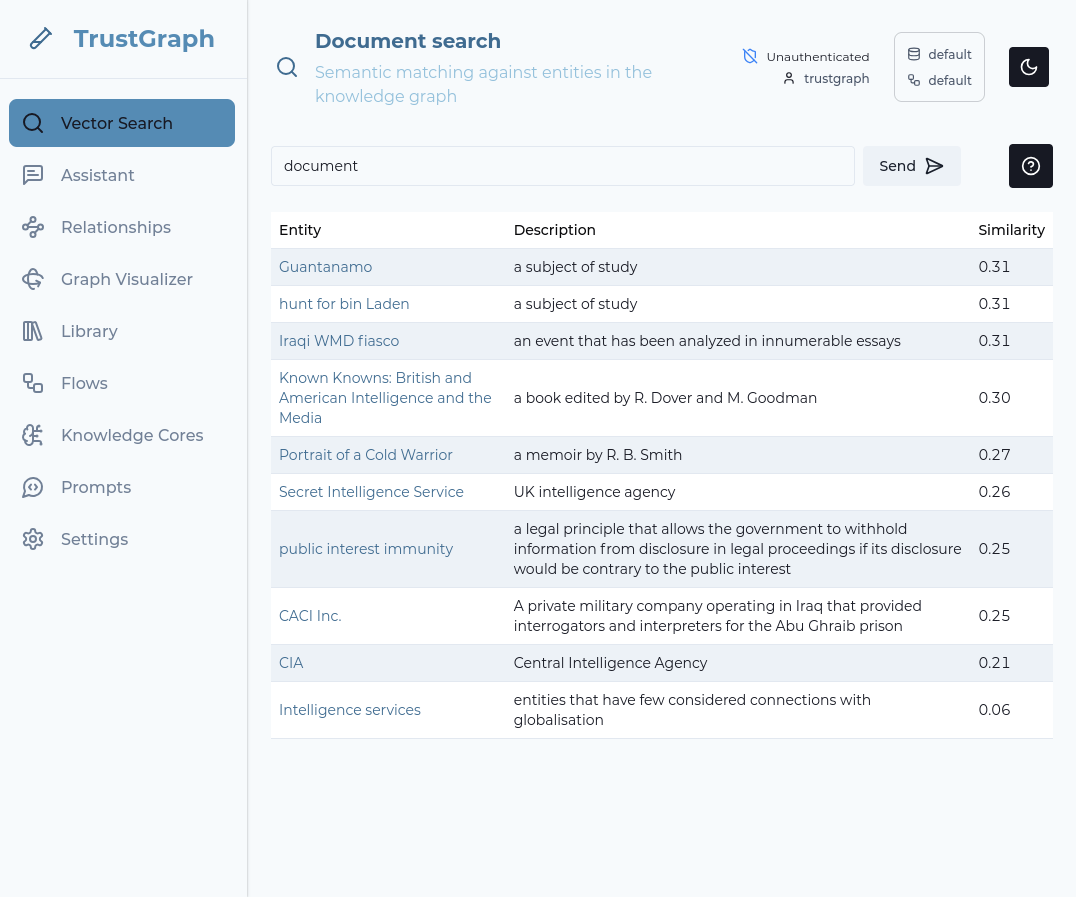
Use Vector search
Select the Vector Search tab. Enter a string (e.g., “document”) in the search bar and hit RETURN. The search term doesn’t matter a great deal. If information has started to load, you should see some search results.
The vector search attempts to find up to 10 terms which are the closest matches for your search term. It does this even if the search terms are not a strong match, so this is a simple way to observe whether data has loaded.
Look at knowledge graph
Click on one of the Vector Search result terms on the left-hand side. This shows relationships in the graph from the knowledge graph linking to that term.
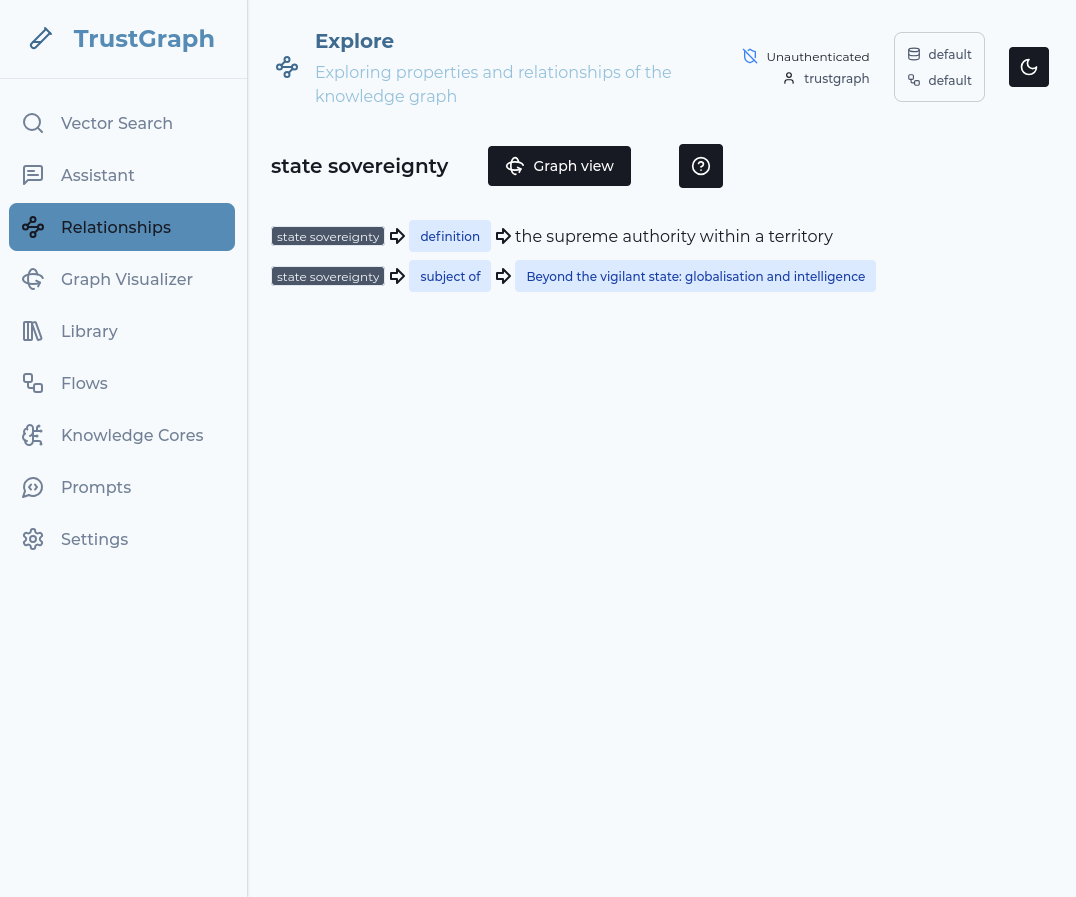
You can then click on the Graph view button to go to a 3D view of the discovered relationships.
Query with Graph RAG
- Navigate to Assistant tab
- Change the Assistant mode to GraphRAG
- Enter your question (e.g., “What is this document about?”)
- You will see the answer to your question after a short period
Troubleshooting
Deployment Issues
Pulumi deployment fails
Diagnosis:
Check the Pulumi error output for specific failure messages. Common issues include:
# View detailed error information
pulumi stack --show-urns
pulumi logs
Resolution:
- Authentication errors: Verify AWS credentials are configured correctly (
aws configure) - Permission issues: Ensure your AWS user/role has necessary permissions (EC2, IAM, VPC)
- Key pair not found: Verify the SSH key pair exists:
aws ec2 describe-key-pairs --key-names trustgraph-key - Quota limits: Check AWS service quotas for EC2 instances, VPCs, and EBS volumes
- Region mismatch: Ensure Bedrock model access is enabled in your deployment region
RKE2 cluster fails to form
Diagnosis:
Check EC2 instance logs:
# Get instance IDs from Pulumi output
pulumi stack output
# SSH to server node
ssh -i ~/.ssh/trustgraph-key.pem ec2-user@SERVER_IP
# Check RKE2 server logs
sudo journalctl -u rke2-server -f
Resolution:
- Verify security group rules allow inter-node communication
- Check that all nodes can reach the RKE2 server node
- Ensure sufficient resources on EC2 instances
- Review cloud-init logs:
sudo cat /var/log/cloud-init-output.log
Pods stuck in Pending state
Diagnosis:
kubectl -n trustgraph get pods | grep Pending
kubectl -n trustgraph describe pod <pod-name>
Look for scheduling failures or resource constraints in the describe output.
Resolution:
- Insufficient resources: Increase instance type or node count in Pulumi configuration
- EBS CSI driver issues: Check CSI driver pods:
kubectl -n kube-system get pods | grep ebs-csi - PersistentVolume issues: Check PV/PVC status:
kubectl -n trustgraph get pv,pvc - Node issues: Check node status and resources:
kubectl describe nodes
AWS Bedrock integration not working
Diagnosis:
Test LLM connectivity:
tg-invoke-llm '' 'What is 2+2'
A timeout or error indicates Bedrock configuration issues. Check the text-completion pod logs:
kubectl -n trustgraph logs -l app=text-completion
Resolution:
- Verify Bedrock model access is enabled in AWS Console for your region
- Check IAM role has Bedrock permissions:
aws iam get-role-policy --role-name trustgraph-bedrock-role --policy-name BedrockAccess - Ensure the model ID is correct in configuration
- Verify region matches between deployment and Bedrock model access
- Check AWS service quotas for Bedrock
Port-forwarding connection issues
Diagnosis:
Port-forward commands fail or connections time out.
Resolution:
- Verify kubeconfig is set:
echo $KUBECONFIG - Check that the target service exists:
kubectl -n trustgraph get svc - Ensure no other process is using the port (e.g., port 8088, 8888, or 3000)
- Try restarting the port-forward with verbose logging:
kubectl port-forward -v=6 ... - Verify RKE2 cluster is healthy:
kubectl get nodes
Service Failure
Pods in CrashLoopBackOff
Diagnosis:
# Find crashing pods
kubectl -n trustgraph get pods | grep CrashLoopBackOff
# View logs from crashed container
kubectl -n trustgraph logs <pod-name> --previous
Resolution:
Check the logs to identify why the container is crashing. Common causes:
- Application errors (configuration issues)
- Missing dependencies (ensure all required services are running)
- Incorrect secrets or environment variables
- Resource limits too low
- AWS credentials not properly configured
EBS volume attachment failures
Diagnosis:
Check EBS CSI driver logs:
kubectl -n kube-system logs -l app=ebs-csi-controller
Resolution:
- Verify EBS CSI driver is installed correctly
- Check IAM permissions for EBS operations
- Ensure availability zone matches between PVC and node
- Check AWS service limits for EBS volumes
AWS-Specific Issues
EC2 instances fail to launch
Diagnosis:
Check AWS EC2 console or CLI:
aws ec2 describe-instances --filters "Name=tag:Name,Values=trustgraph-*"
Resolution:
- Verify AWS service quotas for EC2 instances in your region
- Request quota increases if needed via AWS Console
- Try a different instance type if capacity is unavailable
- Check if AMI is available in your region
- Verify VPC and subnet configuration
Bedrock throttling errors
Diagnosis:
Error messages about Bedrock rate limits or throttling in text-completion logs.
Resolution:
- Check Bedrock quotas in AWS Console under “Service Quotas”
- Request quota increases if needed
- Switch to a different Bedrock model with higher quotas
- Implement request rate limiting in your application
- Consider using provisioned throughput for production workloads
SSH Access to Nodes
To troubleshoot or manage RKE2 nodes directly:
# Get server node IP from Pulumi output
pulumi stack output serverPublicIp
# SSH to server node
ssh -i ~/.ssh/trustgraph-key.pem ec2-user@SERVER_IP
# Common RKE2 commands
sudo systemctl status rke2-server
sudo journalctl -u rke2-server -f
sudo kubectl get nodes
Shutting down
Clean shutdown
When you’re finished with your TrustGraph deployment, clean up all resources:
pulumi destroy
Pulumi will show you all the resources that will be deleted and ask for confirmation. Type yes to proceed.
The destruction process typically takes 8-12 minutes and removes:
- All TrustGraph Kubernetes resources
- RKE2 cluster components
- All EC2 instances
- EBS volumes
- IAM roles and policies
- Security groups
- VPC and networking components (if created by Pulumi)
Cost Warning: AWS charges for running EC2 instances, EBS storage, data transfer, and Bedrock API calls. Make sure to destroy your deployment when you’re not using it to avoid unnecessary costs.
Verify cleanup
After pulumi destroy completes, verify all resources are removed:
# Check Pulumi stack status
pulumi stack
# Verify no resources remain
pulumi stack --show-urns
# Check AWS for remaining resources
aws ec2 describe-instances --filters "Name=tag:Name,Values=trustgraph-*"
aws ec2 describe-volumes --filters "Name=tag:Name,Values=trustgraph-*"
Delete the Pulumi stack
If you’re completely done with this deployment, you can remove the Pulumi stack:
pulumi stack rm dev
This removes the stack’s state but doesn’t affect any cloud resources (use pulumi destroy first).
Cost Optimization
Monitor Costs
Keep track of your AWS spending:
- Navigate to Cost Explorer in AWS Console
- View cost breakdown by service
- Set up billing alerts
Cost-Saving Tips
- Spot Instances: Use EC2 Spot instances for non-production workloads (up to 90% cheaper)
- Right-size instances: Choose instance types based on actual usage
- Reserved Instances: Purchase reserved instances for production (up to 72% savings)
- Stop non-production: Stop dev/test instances when not in use
- EBS optimization: Use gp3 volumes instead of gp2, delete unused snapshots
- Bedrock optimization: Cache responses, implement rate limiting, choose cost-effective models
Example cost estimates (us-west-2):
- 3 x t3a.xlarge instances: ~$0.15/hour each = ~$330/month
- EBS volumes: ~$50-80/month (depends on size and IOPS)
- Data transfer: First 100GB/month free, then $0.09/GB
- Bedrock API: Pay per request (varies by model)
- Total estimated: ~$400-500/month for basic deployment (plus Bedrock usage)
Security Hardening
RKE2 comes with security hardening by default, but additional steps can enhance security:
Network Security
- Restrict security group ingress rules to only necessary ports
- Use AWS WAF for web application firewall protection
- Enable VPC Flow Logs for network traffic analysis
- Consider using AWS PrivateLink for service access
Access Control
- Enable AWS CloudTrail for API activity logging
- Use IAM roles instead of access keys where possible
- Implement least privilege IAM policies
- Enable MFA for AWS console access
- Rotate SSH keys regularly
Compliance
- Run CIS benchmark scans on RKE2 cluster
- Enable AWS Config for compliance monitoring
- Use AWS Security Hub for centralized security findings
- Consider AWS GuardDuty for threat detection
Next Steps
Now that you have TrustGraph running on AWS with RKE2:
- Guides: See Guides for things you can do with your running TrustGraph
- Scale the cluster: Add more agent nodes or increase instance sizes
- Production hardening: Implement additional security controls and monitoring
- High availability: Deploy across multiple availability zones
- Integrate AWS services: Connect to S3, RDS, DynamoDB, or other AWS services
- CI/CD: Set up AWS CodePipeline or GitHub Actions for automated deployments
- Monitoring: Integrate with CloudWatch and AWS X-Ray
- Bedrock models: Explore other Bedrock models (Claude, Mistral, LLaMA, etc.)
- Custom models: Consider Amazon SageMaker for custom model hosting
Additional Resources
- TrustGraph AWS RKE Pulumi Repository - Full source code and configuration
- RKE2 Documentation - Learn more about RKE2
- AWS Bedrock Documentation - Explore Bedrock capabilities
- AWS Well-Architected Framework - Best practices for AWS